Knowledge: What is alloy steel?
Alloy steel is a fascinating material that has revolutionized modern engineering. Imagine a material that can be customized to have specific properties like high strength, corrosion resistance, and durability. It all started in the early 1900s when metallurgists realized that adding different metals and elements to steel can greatly enhance its performance.
Today, alloy steel is used in countless applications, from building skyscrapers to manufacturing surgical tools. But what exactly is alloy steel? How is it made? And why is it so important in our modern world? Join me on this journey as we explore the wonders of alloy steel.
Alloy steel is a type of steel that is made by mixing elements such as manganese, silicon, copper, nickel, chromium, and others with iron to enhance its properties. This results in a material with improved strength, durability, and resistance to wear, corrosion, and heat. Alloy steel is commonly used in a variety of applications, such as construction, machinery, transportation, and more, where high performance and reliability are required.

In this article, we’ll talk about the alloy steel, and provide you with the information from the following aspects:
Contents
What are the different types of alloy steel?
As a manager of a professional export company dealing in alloy steel, I can say that alloy steel is a type of steel that contains other elements apart from iron and carbon. These additional elements are intentionally added to enhance the physical and chemical properties of the steel, such as strength, toughness, and corrosion resistance.
There are many different types of alloy steel, each with its unique combination of elements and properties. Here are some examples of the most commonly used types of alloy steel:
Low-alloy steel: This type of alloy steel contains small amounts of alloying elements, typically less than 5%, and is often used in structural applications.
High-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steel: HSLA steel contains higher levels of alloying elements, up to 10%, and is used in applications where high strength and durability are required, such as in construction and automotive industries.
Stainless steel: This type of alloy steel contains a minimum of 10.5% chromium, which provides excellent resistance to corrosion and oxidation.
Tool steel: Tool steel contains high levels of alloying elements, such as tungsten, molybdenum, and vanadium, which enhance its hardness, toughness, and wear resistance.
Maraging steel: Maraging steel contains high levels of nickel and other elements, which make it highly resistant to stress and cracking.
Nickel-based alloys: These alloys contain high levels of nickel, which provides excellent resistance to heat, corrosion, and oxidation.
Cobalt-based alloys: Cobalt-based alloys are often used in high-temperature and wear-resistant applications.
Titanium-based alloys: These alloys contain titanium and other elements, such as aluminum and vanadium, which provide high strength, corrosion resistance, and low density.
Copper-based alloys: Copper-based alloys are used in electrical and electronic applications due to their excellent conductivity.
Aluminum-based alloys: These alloys contain aluminum and other elements, such as copper and magnesium, which provide high strength and corrosion resistance.
In conclusion, the different types of alloy steel are designed to meet the specific needs of various industries and applications. It is important for our customers to understand the properties of each type of alloy steel to select the right material for their projects.

What are the advantages of using alloy steel over carbon steel?

Well, my dear friend, the advantages of using alloy steel over carbon steel are as clear as day! First of all, alloy steel offers a higher level of strength and toughness, which makes it a great choice for demanding applications in industries such as construction and transportation.
Another advantage of alloy steel is its resistance to corrosion, oxidation, and wear. This is thanks to the addition of various alloying elements, such as chromium, nickel, and molybdenum, which help to protect the steel from environmental damage and prolong its lifespan.
In addition, alloy steel can be customized to suit specific application requirements, as different alloying elements can be added to achieve desired properties such as increased hardness or improved ductility. This makes it a versatile and adaptable material for a wide range of industrial and commercial applications.
So, my friend, if you’re looking for a material that offers strength, durability, and versatility, alloy steel is definitely the way to go!
What are some common applications of alloy steel?
Ah, the versatile alloy steel. Where do I even begin? It’s like the chameleon of metals, adapting to whatever situation it’s in.
One common application of alloy steel is in the manufacturing of tools and machinery. Alloy steel’s strength, hardness, and durability make it ideal for these uses. It can withstand extreme temperatures, resist corrosion and wear, and maintain its shape and structure even under heavy use.
Another application is in the construction industry. Alloy steel is used to make structural parts for buildings, bridges, and other infrastructure projects. Its high tensile strength makes it perfect for these heavy-duty applications.
But wait, there’s more! Alloy steel is also used in the automotive industry, particularly in the production of engines and transmissions. Its ability to withstand high temperatures and pressure makes it an excellent material for these critical components.
And let’s not forget about the energy sector. Alloy steel is used in the production of oil and gas drilling equipment and in power generation plants. Its strength and resistance to corrosion make it a reliable choice for these demanding applications.
In short, the possibilities are endless with alloy steel. From the tools we use to the buildings we live in, alloy steel plays a crucial role in our modern world.
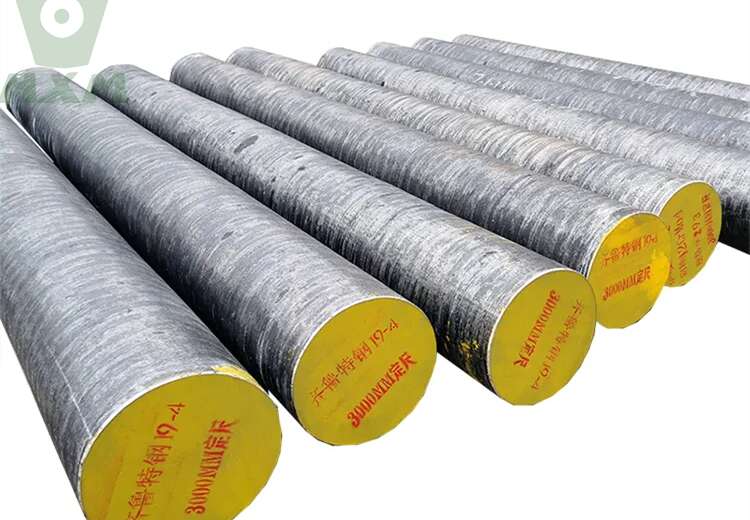

What are the properties of alloy steel?

This incredible material has a plethora of properties that make it a top choice in many industries. Let’s start with its strength – alloy steel is known for being incredibly strong and durable, making it perfect for heavy-duty applications. Its resistance to wear, corrosion, and impact is also worth noting.
But that’s not all. Alloy steel also has impressive heat resistance, which makes it ideal for high-temperature environments. Its versatility allows for a wide range of applications, from construction to manufacturing to aerospace engineering.
And let’s not forget about its machinability. Alloy steel is easily machined, which makes it a top choice for creating intricate and precise parts. It’s also relatively affordable, making it accessible to a wide range of industries.
In short, alloy steel is a jack-of-all-trades when it comes to material properties. Its strength, resistance, and versatility make it a top choice in many applications. If you need a material that can stand up to tough conditions and perform reliably, alloy steel is the way to go.
How is alloy steel made and processed?
Ah, the age-old question of how alloy steel is made and processed. Well, my curious friend, let me tell you a tale of heat, metals, and a touch of magic.
Alloy steel is made by combining iron with other elements such as nickel, chromium, or manganese, to create a material with enhanced properties such as strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion. These elements are added to the molten iron during the steel-making process, and the resulting mixture is then formed into various shapes and sizes using different processing methods such as hot rolling, cold rolling, and forging.
But that’s not all, oh no. The real magic happens during the heat treatment process, where the steel is subjected to extreme temperatures and cooling rates to achieve specific properties such as hardness, toughness, and ductility. It’s like watching a superhero undergo a transformation to become even more powerful!
So, my friend, the making of alloy steel is truly a work of art, combining science and magic to create a material that can withstand the test of time. And the best part? You get to enjoy the benefits of this wondrous creation in your everyday life, from construction to aerospace, and everything in between.
How does the composition of alloy steel affect its properties?

Alloy steel is made by adding other elements to iron and carbon, which changes its chemical makeup and ultimately affects its properties.
For example, adding chromium to the mix can make it more resistant to corrosion, which is why it’s often used in applications where it will be exposed to moisture or other harsh conditions. Molybdenum can improve its strength and toughness, while nickel can improve its ductility and toughness at low temperatures.
But it’s not just about the type of elements added. The amount and ratio of each element can also make a big difference. Too much of one thing or too little of another can completely change the steel’s properties.
It’s like baking a cake – adding just the right amount of each ingredient is key to getting a delicious and perfectly textured cake. The same goes for alloy steel. A carefully crafted recipe of elements and proportions can result in a steel that’s strong, durable, corrosion-resistant, and perfect for a variety of applications.
What is the difference between low-alloy steel and high-alloy steel?
Well, my friend, let me tell you that it all comes down to the amount of alloying elements present in the steel.
Low-alloy steel contains relatively low levels of alloying elements, usually less than 5% by weight. High-alloy steel, on the other hand, contains higher levels of alloying elements, typically more than 5%.
But wait, there’s more! The specific alloying elements used can also vary between low and high-alloy steels. Low-alloy steels may use elements such as nickel, chromium, and molybdenum, while high-alloy steels may incorporate even more exotic elements like tungsten, cobalt, and vanadium.
So, what does this mean for their properties? Well, low-alloy steels tend to have improved mechanical properties compared to carbon steel, such as increased strength and toughness. High-alloy steels, with their greater amount and variety of alloying elements, can have even more impressive properties such as corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength.
In summary, the difference between low-alloy steel and high-alloy steel is primarily the amount and types of alloying elements present. And the more alloying elements, the more potential for some pretty impressive properties.

How does the cost of alloy steel compare to other types of steel?

Now, let’s start by saying that alloy steel is not your average Joe steel. It’s a special blend of metals that can provide unique properties and performance advantages. So, naturally, it’s going to be a little pricier.
But, before you start worrying about breaking the bank, let me assure you that alloy steel is still quite affordable. In fact, its cost is comparable to other high-performance materials like stainless steel and tool steel.
Plus, when you consider the long-term benefits and savings that come with using alloy steel in high-stress applications, the cost is a no-brainer. You’ll have less downtime, fewer replacements, and less maintenance, which translates to more money in your pocket in the long run.
So, don’t be scared off by the initial sticker price of alloy steel. Think of it as an investment in quality and performance, and let the benefits speak for themselves.
Conclusion
In conclusion, alloy steel is a highly versatile and valuable material in various industries. Its unique properties and characteristics make it suitable for a wide range of applications, from aircraft manufacturing to construction. Unlike carbon steel, alloy steel is highly resistant to corrosion, fatigue, and wear, making it more durable and long-lasting.
The different types of alloy steel provide manufacturers with a range of options to choose from, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. From low-alloy to high-alloy steel, there is an alloy that can meet specific needs and requirements.
While alloy steel may be more expensive than carbon steel, its superior properties and performance make it a worthwhile investment. And with advancements in technology and processing techniques, the cost of alloy steel has become more competitive over time.
Overall, alloy steel is an essential material for modern manufacturing and construction. Its unique combination of strength, durability, and versatility has made it an indispensable component in many critical applications.
Request A Free Quote
We’d like to work with you
If you require further information about our metal sheet products or architectural projects, please don’t hesitate to leave your contact details and message here.
Our team of experts will respond within 24 hours to continue the discussion and provide you with any additional information you requires.







